Peptide Bond Of Amino Acids
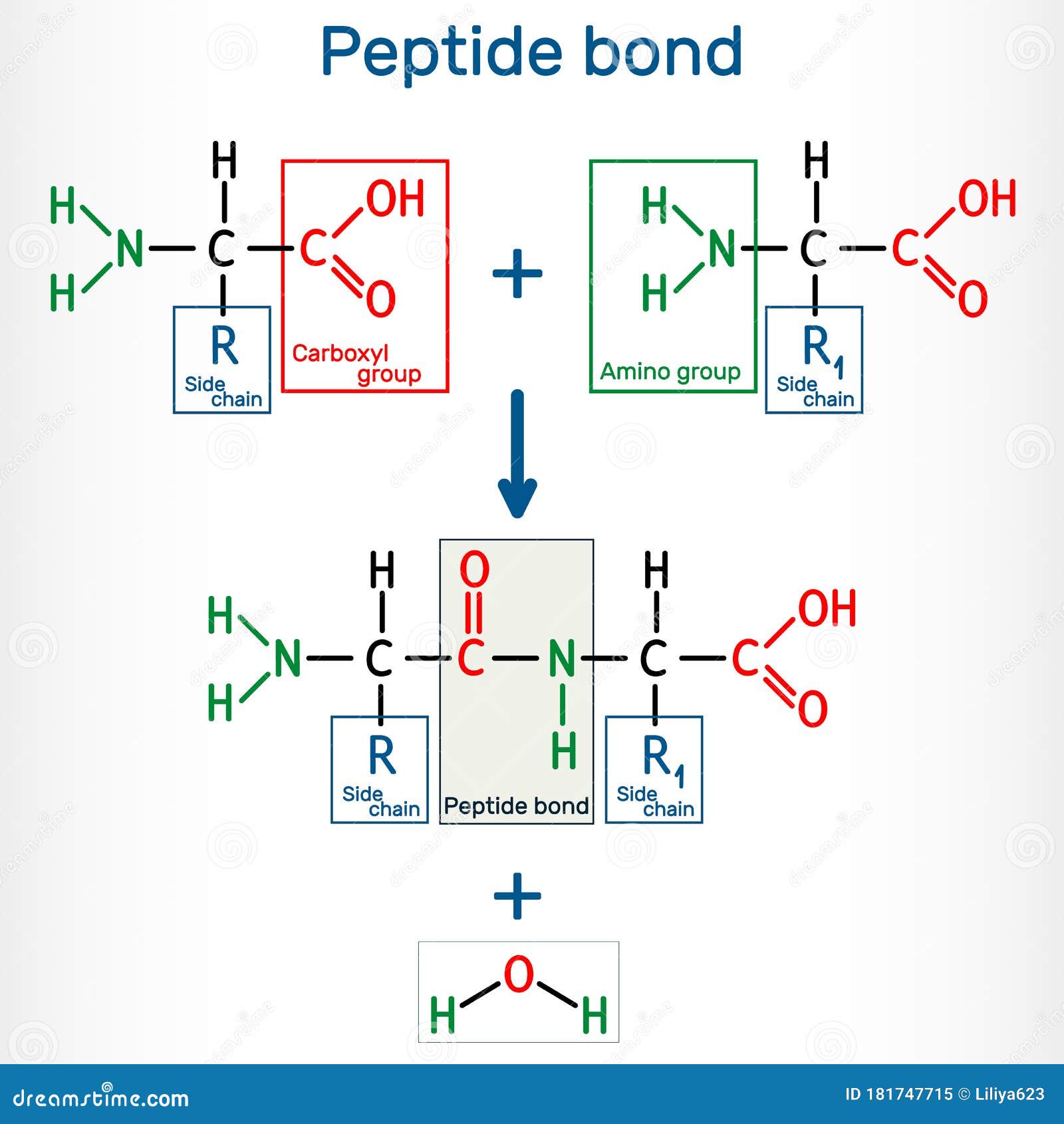
Peptide Bond Of Amino Acids. A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (h2o). When two amino acids are covalently attached by a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine and release a molecule of water.
The amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, which are formed via dehydration reactions. The combining of two amino acids, to form the dipeptide, is accompanied by the loss of one molecule of water. The formation of peptides is nothing more than the application of the amide synthesis reaction.
The combining of two amino acids, to form the dipeptide, is accompanied by the loss of one molecule of water. Nucleotides make up dna and rna, not proteins.
The formation of peptides is nothing more than the application of the amide synthesis reaction. Peptide bond formaion or amide synthesis:
Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Tyr, trp and phe can absorb in the uv region because of.

Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Nucleotides make up dna and rna, not proteins.

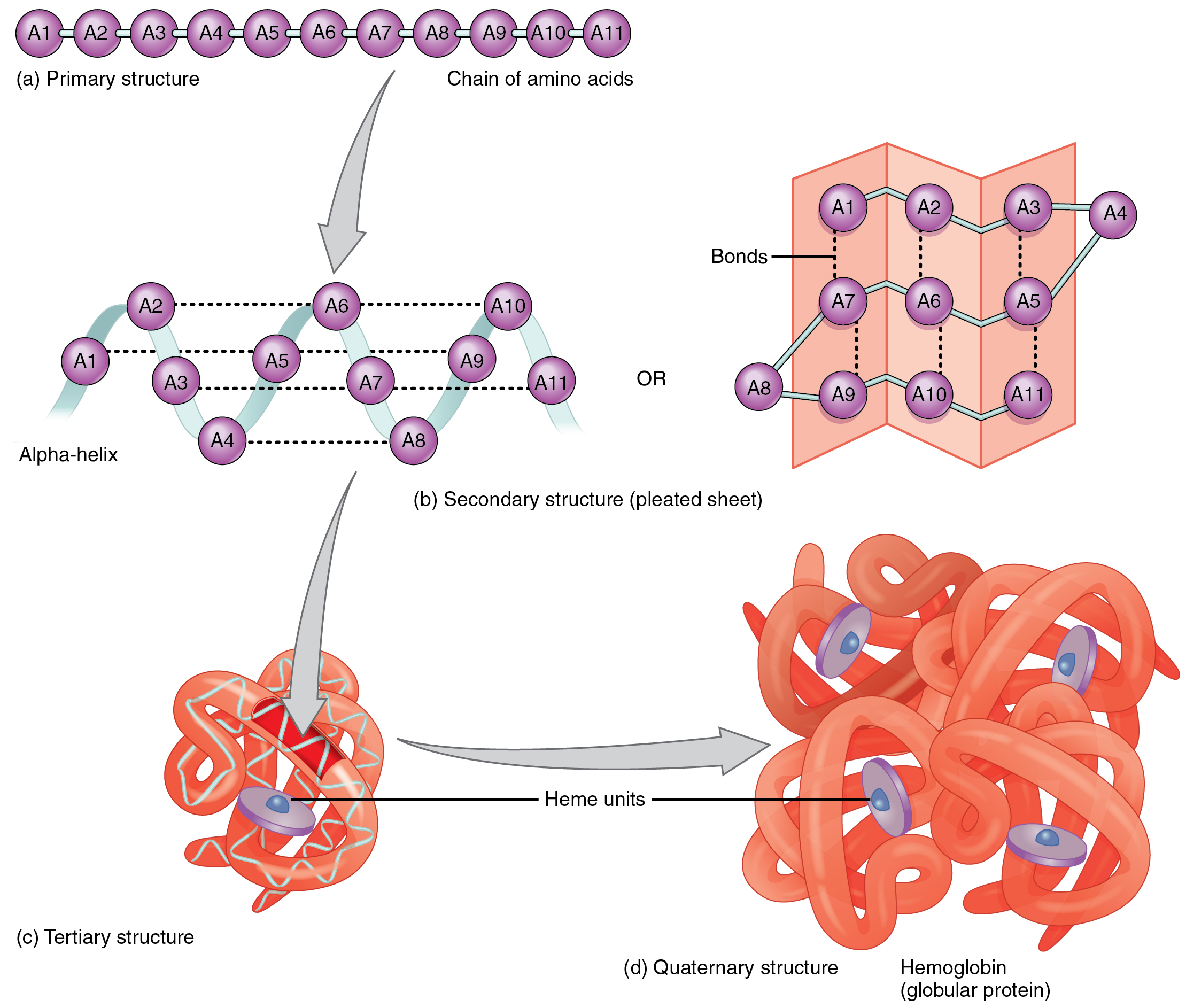
Secondary structure refers to the local folding of the polypeptide chain. By convention, the amide bond in the peptides should be made in the order that the amino acids are written.
Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Clearly, differences between amino acids are defined by the differences between

A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids. Secondary structure refers to the local folding of the polypeptide chain.
Peptides are short chains of amino acids. Second, to calculate a molecular weight,.

By convention, the amide bond in the peptides should be made in the order that the amino acids are written. When two amino acids are covalently attached by a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine and release a molecule of water.
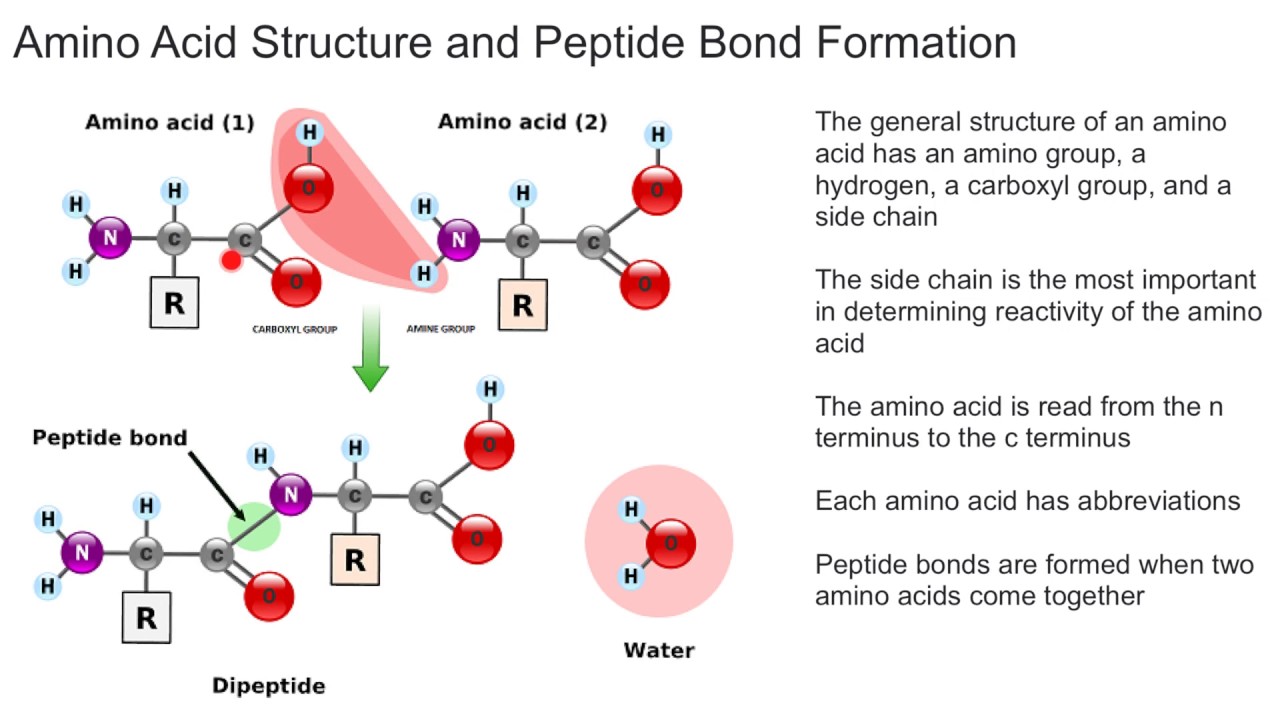
Peptide bonds each amino acid is attached to another amino acid by a covalent bond, known as a peptide bond. A peptide is a short string of 2 to 50 amino acids, formed by a condensation reaction, joining together through a covalent bond.[1] sequential covalent bonds with additional amino acids yield a peptide chain and the building block of proteins.
A peptide is one or more amino acids linked by chemical bonds. Clearly, differences between amino acids are defined by the differences between
The term also refers to the type of chemical bond that joins the amino acids together. Peptide bonds form through a process known as dehydration synthesis.

First of all, your terminology is a bit weird. To form a peptide bond, a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid.
• during protein synthesis, the carboxyl group of amino acid at the end of the growing polypeptide chain reacts with the amino group of an incoming amino acid, releasing a molecule of water. A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (h2o).

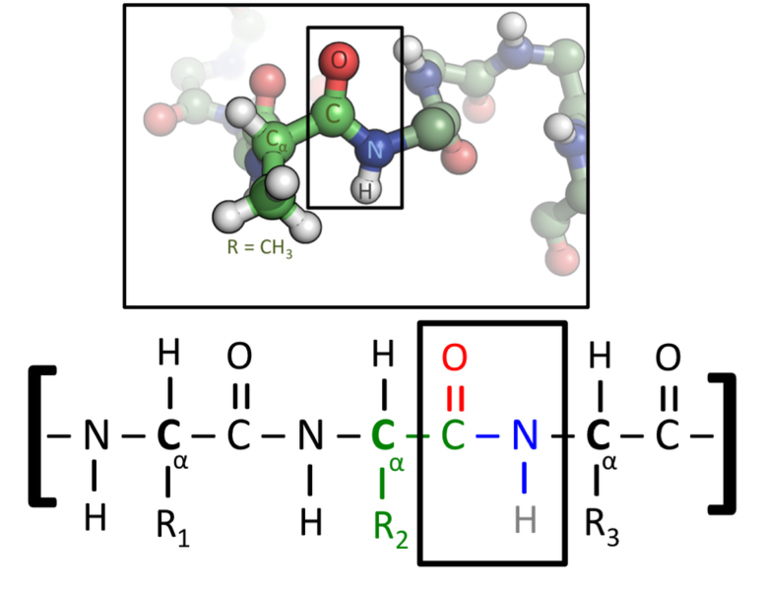
The peptide bond (known generically in organic chemistry as an amide bond). Peptide bonds • amino acids are linked together by 'amide groups' called peptide bonds.

As a result, a molecule of water is also released. A partial double bond exists between carbon and nitrogen of the amide bond which stabilizes the peptide bond.
In dehydration synthesis, a chemical bond is formed through the loss of a water molecule. By convention, the amide bond in the peptides should be made in the order that the amino acids are written.
By convention, the amide bond in the peptides should be made in the order that the amino acids are written. The peptide bond (known generically in organic chemistry as an amide bond).

A peptide is a short string of 2 to 50 amino acids, formed by a condensation reaction, joining together through a covalent bond.[1] sequential covalent bonds with additional amino acids yield a peptide chain and the building block of proteins. A partial double bond exists between carbon and nitrogen of the amide bond which stabilizes the peptide bond.

Amino acids in proteins (or polypeptides) are joined together by peptide bonds. Protein primary structure is defined by the order of amino acids that make up the protein.
First Of All, Your Terminology Is A Bit Weird.A bond does not have a molecular weight. When two amino acids are covalently attached by a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine and release a molecule of water. Only molecules have molecular weight, and that would include the atoms at either end of the bond.
A Peptide Is One Or More Amino Acids Linked By Chemical Bonds.Protein primary structure is defined by the order of amino acids that make up the protein. A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (h2o). The formation of peptides is nothing more than the application of the amide synthesis reaction.
When Two Amino Acids Are Covalently Attached By A Peptide Bond, The Carboxyl Group Of One Amino Acid And The Amino Group Of The Incoming Amino Acid Combine And Release A Molecule Of Water.Peptide bonds form through a process known as dehydration synthesis. To form a peptide bond, a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid. Second, to calculate a molecular weight,.
• During Protein Synthesis, The Carboxyl Group Of Amino Acid At The End Of The Growing Polypeptide Chain Reacts With The Amino Group Of An Incoming Amino Acid, Releasing A Molecule Of Water.The term also refers to the type of chemical bond that joins the amino acids together. Clearly, differences between amino acids are defined by the differences between Peptide bonds • amino acids are linked together by 'amide groups' called peptide bonds.
Peptide Bond Formaion Or Amide Synthesis:As a result, a molecule of water is also released. Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that exist between any two amino acids resulting in a peptide chain. In the presence of atp, ubiquitin is first activated via formation of a thioester bond between.
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Peptide Bond Of Amino Acids"
Posting Komentar